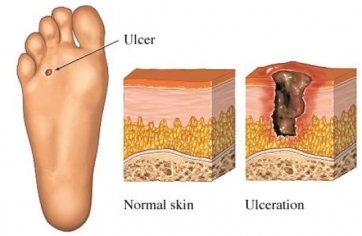
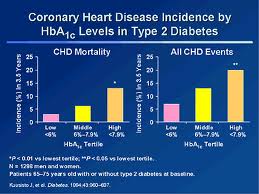
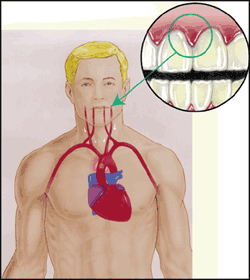
Gene therapy is the new buzzword in a hope for cure of disease, and genetic tests also assist in predicting the risk for disease.
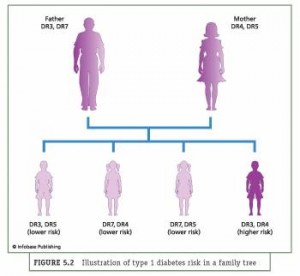
These predictions are reaffirmed by research that comes from McGill University in Montreal under Dr. Constantin Polychronakos, a professor of pediatrics and human genetics. A new DNA chip has been used for testing the genetic makeup that produces diabetes type 1 (also called Juvenile Diabetes). So far the analysis has confirmed four previously identified genetic locations that contribute to the development of diabetes 1, and the test identified a new location occupied by the gene.
With the research team working on the discovery of all the remaining genes, they are confident to develop a test which will predict the risk of developing diabetes. According to Dr. Polychronakos the findings will influence future treatment options. The most promising treatment for those already diagnosed with diabetes1 are stem cell regenerative treatments, such as islet transplantation, since the Langerhans islets are responsible for the production of insulin in the pancreas.
These therapies will only work if the immune system is also treated, so the patient does not suffer a relapse of the disease. Once all the diabetes genes are identified, there will not only be fast screening but also therapies that can be targeted more effectively.
Reference: The Medical Post, August 7, 2007, page 1 and 60 of the Medical Post
More on genetics and diabertes: http://www.who.int/genomics/about/Diabetis-fin.pdf
Last edited December 5, 2012