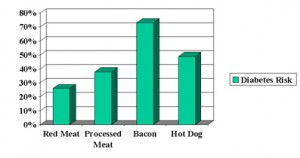
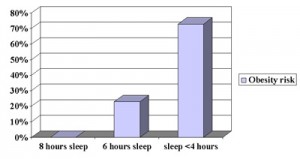
Environmental factors and ethnic customs can influence us to have certain likes and dislikes of foods, but researcher Ahmed El-Sohemy has found in his studies that there is also a biological and genetic basis for some of our food preferences. Researchers from the University of Toronto have discovered a genetic difference in people who consume extra sugar in their diet. The specific genetic constellation which the researchers have called GLUT2 does not only work in the pancreas, but it also is responsible for turning on satiety signals in the brain. It seems to have an impaired ability to notice high blood sugar levels that ultimately send “stop eating” signals to the brain. The habit to eat more sweets has been researched in persons with diabetes, but Dr. El-Sohemy does not believe that diabetes is directly connected with gene GLUT2. On the other hand he does not suggest that the presence of the gene should be an excuse to overindulge in sugar high foods. He states that food habits in humans are often connected to the availability of foods: if there is a birthday party and birthday cake, the people with a liking of sweets will be the first to get a slice of cake. On the other hand, if there are no sweets available, they will not make an extra trip to the store just for a piece of cake. The most logical approach is to minimize the availability of foods that are high in sugar, which is especially important for individuals who have GLUT2, the ”sweet tooth gene”, so they are not tempted to overindulge.
Much was learnt from two separate studies that involved 100 older adults on the one hand who were overweight or obese and 587 healthy younger adults who were mostly lean. Foods and beverages that were consumed were carefully recorded. In both investigations blood was drawn for DNA analysis and the presence or absence of the variation of the GLUT2 gene was compared to the food intake data. The older obese group with the variant gene consumed 112 grams of sugar per day versus 86 Grams per day for the non-variant gene group (normal control). The younger population carrying the variant gene consumed 131 Grams of sugar per day, while the non-variant control of young people consumed 115 Grams of sugar per day. This illustrates how genetic influences have an effect on our eating habits and also that younger people ought to be careful that they do not overuse sugar containing foods.
It also points to the solution of controlling your weight, if you belong to the higher risk group with the GLUT2 gene: you must exercise more to burn up the extra calories you tend to eat. A brisk walk on a treadmill will consume about 300 or 350 Cal in 30 minutes depending on the slope and the miles per hour setting.
Reference: Medical Post Vol 44, No. 16, June 16, 2008: page 19 (based on May issue of Physiological Genomics)
Last edited December 4, 2012