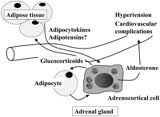
Fat cells are known to secrete a number of substances that affect the lining of the arteries and that are also known to be associated with the metabolic syndrome. One of the observations that physicians were aware of for some time is that aldosterone, a hormone from the adrenal glands, is often elevated in patients with high blood pressure and obesity or people who are overweight.
Dr. Ehrhart-Bornstein and her group from the University Medical Center, Heinrich Heine University of Düsseldorf in Germany investigated this interaction between fat cell metabolites and the cells of the adrenal cortex in more detail. They used a tissue culture model with human adrenocortical cells (NCI-H295R). To their surprise they found two separate hormone factors that were produced by fat cells and that showed in the tissue culture system a 7-fold increase in aldosterone hormone release. As aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid hormone they called these new releasing hormones mineralocorticoid-releasing factors. Further characterization of these factors demonstrated that one was of a higher molecular structure and was heat-sensitive, the other one was smaller in size and was more heat resistant. Each factor alone lost much of the aldosterone releasing activity, but when recombined they had 93% of the original action. Synthesis of messenger RNA inside the adrenocortical cells was stimulated by a factor of 10-fold from the action of the mineralocorticoid-releasing factors. Other hormones were also somewhat stimulated such as release of cortisol by a 3-fold increase and DHEA by a 1.5-fold increase. Other known substances from fat cells were entirely ineffective in this testing system.
When asked how this new research might fit in with the observation that loss of fat through calorie restriction has a beneficial effect on high blood pressure, the authors commented that with less fat storage in fat cells during weight loss the production of mineralocorticoid-releasing factors would go down significantly and aldosterone would be released at a much lower rate thus decreasing blood pressure through the aldosterone/angiotensin/renin mechanism.
Nov. 12, 2003 paper on which this write-up is based: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC283571/
Last edited October 26, 2014