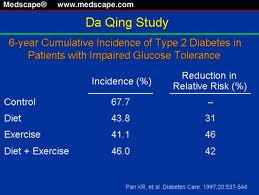
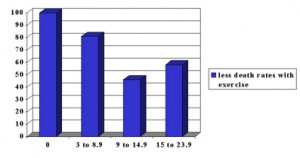
Generally it is assumed that persons in their thirties and forties should be in their prime, and health concerns are cropping up in the higher middle age or only in old age.
Also, women were thought to generally enjoy better health and life expectancy, but the large Nurses’ Health Study on 77,782 women in the age group of 34 to 59 years shows other aspects.
Even in females who had no heart problems and no cancer at the onset of the study, lifestyle choices can make it or break it. At the end of the study that spanned 24 years, it became obvious that a total of 28% of all the mortalities could be attributed to smoking. If risky lifestyle choices were combined in the form of smoking, being overweight, having a lack of physical activity and a qualitatively poor diet, this number jumped to 55%. Alcohol intake did not change this estimate significantly.
It is obvious that for the benefit of better health and less mortality in middle age women, diet, exercise, a healthy body weight and eradicating smoking are key factors.
Reference: BMJ 2008;337:a1440
Comment on Nov. 18, 2012: So how many years longer will a woman live, if she quits at age 30? The Million Women Study found out that she will live 10 years longer than the control group of smoking women (see link). Nothing has changed since 2008. Lifestyle issues remain at the forefront.
Last edited December 3, 2012