Numerous medications for blood pressure control are in circulation. Treatment of high blood pressure patients is crucial in the prevention of strokes, but despite the multitude of drugs that are on the market, the treatment has its challenges. Some of the drugs have side effects, like an irritating cough, and a suitable medication has to be tried out first. Even, when all is well and there are no unpleasant side effects, many patients have a problem with compliance. Pills that have to be taken several times per day are forgotten. As a result, the patient will have poor blood pressure control.
Blood pressures must be controlled on an ongoing basis. Ideally there are no big fluctuations, whether it is day or night. For this purpose, a medication has to stay in the system of the patient long enough. This time stretch is called the half-life of a drug.
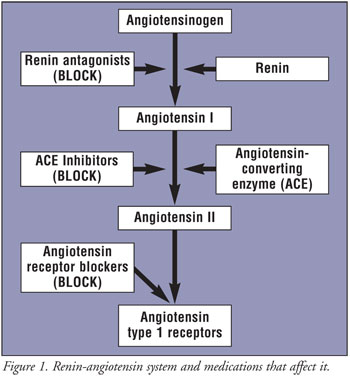
The first drug in a new class of agents for the treatment of high blood pressure does exactly that: it has a long half-life, so blood pressure control is smooth and continuous, day or night. The oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren has the potential to protect the heart and other organs with a once-daily dosage of 150 mg or 300 mg. The drug is being developed by Novartis, and clinical trials are on their way.
The medication in combination with a diuretic provides significant additional blood pressure reduction. The agent at work is a renin inhibitor (also known medically as “renin antagonist” as it blocks the effects of renin). In the past, renin inhibitors for treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure) could only be used as intravenous solution and this was only effective for a short time.
The new development is a breakthrough, as the medication is taken by mouth and it continues to work even when the drug is gone from the blood stream. It is ideal for daily dosing, and there is no apparent buildup in the body.
More information about hypertension (high blood pressure): http://nethealthbook.com/cardiovascular-disease/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/
Reference: The Medical Post, June 13, 2006, page 38
Comment on Nov. 13, 2012: Aliskiren (brand name “Tekturna”) was approved by the FDA in March of 2007. However, as all drugs, it does have some side-effects like headaches, cough, angioedema, skin rash, elevated uric acid with gout etc. (see this Wikipedia link).
Last edited Nov. 1, 2014