A recent publication in the British Medical Journal was reviewed in the Aug.10 issue of The Medical Post. The study was concerning detailed census data from New Zealand where two cohorts of the population were compared in 1981 and 1996.
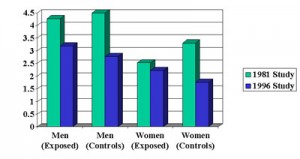
The 1981 study involved 286,796 people, the 1996 study involved 382,462 people. Both cohorts were further classified into exposure to second hand smoke and non-exposure meaning that they lived in a smoke-free home (controls). I have elected to show the results in a graph below for ease of reference. The authors Dr. Tony Blakely and others from the University of Otago had followed each cohort for 3 years and recorded death rates (mortality rates) for each of the subgroups.
They pointed out that there was a 15% increase in premature death for those exposed to second hand smoke when compared to the controls who were not exposed.
Comments: 1. The mortality in the 1996 study (in blue bars in the graph below) for males is what the authors quoted (15.1%). However, for females, the death rate was even higher with regard to exposure to second hand smoke: mortality was 26.7% higher when the exposed group is compared to the controls.
2. The 1981 study (green bars in the graph below) had a much higher overall mortality than the overall mortality in the 1996 study (blue bars). This likely is due to the 15 year interval between the two study groups and the fact that during that time in New Zealand as in many other industrialized countries the death rate from cigarette smoke exposure has declined significantly.
One such study indicates a reduction between 1981 and 1997 of 38% in all preventable deaths, which includes death as a result of exposure to cigarette smoke. The average death rate reduction in the New Zealand study over the 15 years was 31.7% for men and 29.35% for women when the exposed groups and control groups were pooled.
3. The controls and the relationship of the subgroups within the 1996 study (the blue bars in the graph below) were very consistent , but were not consistent within the 1981 study (green bars).
For instance, the controls of death rates should always be smaller in both males and females when compared to the groups that were exposed to second hand cigarette smoke. In the 1996 study this was the case, but in the 1981 study this was not the case. This may indicate that there were other negative factors included in the 1981 study leading to premature death or that the controls were simply also exposed to cigarette smoke in the past.
| Mortalitiy Rates (%) Resulting From Exposure to Second Hand Smoke in New Zealand Study |
 |
Conclusion: This is an important study as it is based on large numbers and it shows that even relatively small concentrations of cigarette smoke in the environment make a measurable difference in terms of death rates among the population. It also confirms the fact that the death toll has been reduced by about 30% in the population within 15 years (between 1981 and 1996), because many people have quit smoking during that time period and this is measurable as indicated above (green bars higher on average than blue bars).
More info on:
Heart attacks: http://nethealthbook.com/cardiovascular-disease/heart-disease/heart-attack-myocardial-infarction-or-mi/
Lung cancer: http://nethealthbook.com/cancer-overview/lung-cancer/
Reference: The Medical Post, Aug. 10, 2004, page 48
Last edited October 27, 2014