Recently another news story about a failed drug against Alzheimer’s disease (AD) went through the news media as shown in this link.
Donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine are the most common drugs used to attempt to treat Alzheimer’s as this review explains. None of these drugs are a real breakthrough with regard to truly curing AD, as the drugs only achieve a few months of delay in the eventual deterioration of the AD patient’s symptoms. On the other hand there is an overwhelming accumulation of data in the last few years showing that many different factors can prevent AD and dementia. Below I am reviewing all these preventative factors and steps.
Genetic and epigenetic factors in Alzheimer’s disease
Early onset Alzheimer’s disease occurs between 30 and 60 years of age. It is due to a genetic predisposition (mutations on genes of chromosomes 1, 14 and 21). Only about 5% of all AD cases are caused this way. The remaining 95% of Alzheimer’s cases are due to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Here the causation is due to a combination of genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors. One genetic risk factor in this group is important, namely the apolipoprotein E gene (APOE), which is located on chromosome 19. There are several forms of APOE as this review explains. It also states that there is so much variation between the various APOE forms and even the worst form of this does not necessarily mean that the person who has this will come down with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. So APOE is presently only used in research projects. Your doctor will only order genetic tests in people who have a strong family history of early onset AD.
There is another genetic marker, the CYP46 gene that was found to be present in some late-onset AD patients. If it is combined in a patient with the APOE gene, there is a much higher chance of developing AD as this review shows.
Epigenetic factors are probably more important than genetic factors for most cases of late-onset AD, as this review explains. Another review came to the same conclusion.
What are epigenetic factors? Exercising, replacing missing hormones, using a calorie restricted, only 15-20% fat containing diet; and taking supplements as listed below that will keep harmful genes in the “off” position and protective genes in the “on” position. Taking these preventative steps is probably more powerful than using any of the presently available medications mentioned above.
Exercise, diet, control blood pressure
As already mentioned, these are some of the powerful epigenetic factors that will prevent AD down the road. Controlling blood pressure has long been known to improve cognitive function. It is now evident that there seems to be a problem with microcirculation in brain tissue before it comes to neurodegenerative changes of AD and the underlying deficiency in nitric oxide production in the lining of the diseased arteries. Other research has shown that a lack of nitric oxide (NO) production is also the underlying problem with hypertension.
Green vegetables such as kale, spinach, also cabbage varieties and red beets are a source of nitric oxide and have also been shown to prevent AD at the same time.
Add to this exercise and you have a winning combination for the prevention of AD. You guessed right: exercise increases NO production from he lining of your arteries. When people age their lining of the arteries does not produce as much NO as in younger years. However, there is a supplement available, Neo40 Daily, that can be taken twice a day to compensate for this.
Here is another report about a 30% to 40% reduction in the incidence of AD when people do regular, simple exercises.
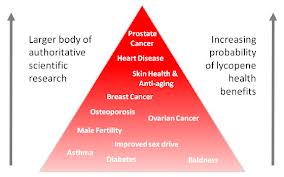
More good news about fruit and vegetables: tomatoes, watermelons, pink guava, pink grapefruit, papaya, apricot and other fruit all contain lycopenes, which have been shown to prevent AD.
Recently a new testing tool in combination with a PET scan of the brain has been developed, which may help the treating physicians to assess improvement or deterioration of an AD patient objectively using this method. However, this is still considered to be only a research tool at this time.
Supplements to prevent Alzheimer’s disease
The following brain-specific nutrients play a part in the prevention and treatment of AD (according to Ref.1):
1. B-vitamins: they are important to support the energy metabolism of brain cells.
2. Vitamin C: this has antioxidant properties and prevents brain cells and supportive glia cells from oxidizing.
3. Vitamin E in the form of mixed tocopherols: together with vitamin C has been shown to prevent Alzheimer’s disease
4. Phosphatidylserine (PS), with an intake of up to 300mg/day: counteracts and prevents memory loss.
5. Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone), 100mg/day (it would be safe to take 400 mg per day, which is also cardio protective): stabilizes the mitochondria of brain cells and heart muscle cells. It is a powerful neuroprotective agent and supports ATP production (energy metabolism of brain cells).
6. Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba), at a dose up to 240mg/day: increases micro vascular circulation, neutralizes free radicals from oxidation and improves short-term memory.
7. Omega-3 fatty acid and DHA, 1500mg/day: has anti-inflammatory properties.
Other nutrients that hold promise are:
8. Huperzine A, 100 to 200mg/day: natural anticholinesterase inhibitor, derived from the Chinese club moss, surpasses donezepil according to studies by doctors in China
9. Vinpocetine, 2.5 to 10mg/day: comes from the periwinkle plant, increases cerebral blood flow and stimulates brain cell metabolism
10. Turmeric extract (curcumin) is very beneficial in reducing tau protein deposits in AD.
All these statements and dosages are cited from Ref.1.
Hormones to prevent Alzheimer’s disease
According to Ref. 1 there are certain hormones that can prevent AD: DHEA, pregnenolone, estrogen (bioidentical estrogen only).
- DHEA is persistently low in AD patients and replacement with DHEA at 50 mg daily has shown improvements in muscle strength and energy of AD patients.
- Pregnenolone has been shown to be a powerful memory enhancer in animals and humans alike.
- Estrogen, if taken as bioidentical estrogen cream (Bi-Est) can improve brain function. Estrogen is a strong epigenetic switch that keeps a woman mentally younger for longer, but has to be balanced with bioidentical progesterone cream to prevent breast cancer and uterine cancer. A study showed that estrogen replacement early in menopause will cut down on the heart attack rates, but it is also known, particularly when given as bioidentical hormone cream to prevent AD.
- In addition progesterone has been described to be of value in the aging woman to preserve brain metabolism.
- Testosterone is known to protect against Alzheimer’s disease in the aging male.
- Melatonin at a starting dose of 1 mg to 3 mg at bedtime often helps to restore the disturbed sleep pattern, but also augments the effects of the other hormones (Ref.1).
Removal of toxins, particularly mercury
Mercury is extremely toxic in minute amounts and affects brain cells preferentially. Intravenous vitamin C/glutathione treatments as described in this blog will remove mercury from your system including the brain.
It may take 20 to 30 such treatments in weekly intervals followed by a maintenance program every two to three weeks to remove mercury from the body.
Other heavy metals can accumulate in the brain as well and must be removed. This is described here in more detail.
Conclusion
There have been major breakthroughs in prevention of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia over the past few years, many unnoticed by the media. The search is still on for an effective drug that would treat AD when it is present. However, this may be 10 or 15 years away and we cannot afford to wait that long. Instead I suggest that people should embrace the concept of preventing AD by using as many of the factors described above. Both at the 2011 and the 2012 Anti-Aging Conferences in Las Vegas several speakers pointed out that a combination of several preventative factors will be much more effective than one factor alone and they estimated that about 80% of AD could be prevented this way.
References
Ref.1. Rakel: Integrative Medicine, 3rd ed., Copyright © 2012 Saunders, An Imprint of Elsevier. Chapter 9 – Alzheimer Disease. Integrative Medicine: “Kirtan Kriya, Telomeres, and Prevention of Alzheimer Disease”, by Dharma Singh Khalsa, MD
Last edited Dec. 18, 2014