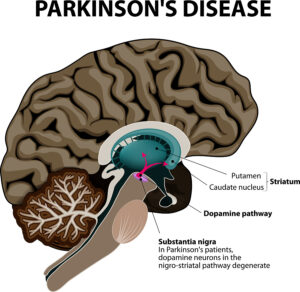
This article explains how the immune system affects Parkinson’s disease (PD). Notably, in the past physicians thought that Parkinson’s disease was due to a degenerative change of the substantia nigra. This explained why balancing was a problem, why shaking of the hands occurred and why falls happened often. It it important to realize that nobody thought about the immune system. And no-one knew that an autoimmune process could be behind Parkinson’s disease.
T cells that react to a damaged protein called alpha-synuclein
There are specific changes in the immune system approximately 10 years before Parkinson’s disease symptoms occur in patients who come down with the disease. Researchers from the La Jolla Institute for Immunology showed that T cells play a key role in causing PD. They react to a damaged protein called alpha-synuclein build up in the dopamine-producing brain cells. Laboratory physicians can assay this through a simple blood test, which becomes a screening tool for early Parkinson’s disease. The reactive T cells stay around for about 10 years, then fade away. There seem to be other immune factors that weaken the initial aggressive phase of the T cells.
The role of inflammation in Parkinson’s
When the immune system malfunctions chronic inflammation can develop. In farmers exposed to pesticides the later development of Parkinson’s disease was observed. The researchers thought that the pesticides caused an irritation of the immune system leading to chronic inflammation. There is evidence that the gut bacteria are different in Parkinson’s disease patients when compared to normal controls. The gut absorbs the metabolites of the abnormal gut bacteria and causes chronic inflammation. In an attempt to stop the inflammatory process, the immune system can develop autoimmune antibodies, which can cross react with cells of the substantia nigra. This in turn can cause Parkinson’s disease.
Lifestyle factors that people can change to prevent PD
Dr. Rebecca Gilbert, vice-president and chief scientific officer for the American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA) commented on the importance of lifestyle changes. She said: “It makes intuitive sense that instituting lifestyle modifications that potentially decrease inflammation may decrease the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Exercise, for example, has been shown to reduce inflammation and is probably one of the many reasons that exercise reduces the risk of Parkinson’s disease and also improves established Parkinson’s disease.” She commented further: “Also, we should avoid things like excessive alcohol and nicotine that we know have negative effects on the immune system,” she added. “And managing our stress as best as possible can slow and help maximize outcomes of many diseases.”
Changing diet can help postpone Parkinson’s disease
With regard to the best diet that will help Parkinson’s disease patients she said: “The MIND diet emphasizes whole grains, vegetables, nuts, legumes, and berries. Fish is the preferred protein and olive oil is the preferred fat. Recently a study showed that adherence to the MIND diet and the Mediterranean diet had an association with later onset of Parkinson’s disease.”
The gut connection to Parkinson’s disease
According to the WHO the global prevalence of Parkinson’s disease has doubled in the last 25 years. At this point we do not know why this is so. But many investigations have shown that there is a significant difference in the gut bacteria composition of healthy controls and Parkinson’s disease patients. There is a 30% difference between the bacterial composition of healthy controls and patients with Parkinson’s disease. This has led to Braak’s Hypothesis of Parkinson’s Disease. This hypothesis says that an unknown pathogen enters through the nose, the person swallows it and it ends up in the gut. Absorption gets it into the gut wall and it migrates through the vagus nerve into the central nervous system where it leads to accumulation off alpha-synuclein in the substantia nigra. This destroys the dopamine producing cells in that region causing the symptoms of PD.
Can any diet fight gut dysbiosis?
- In 2022 study they found that flavonoids, the pigments of fruit were associated with a lower mortality of patients with Parkinson’s disease.
- In an earlier study of 2018 researchers determined that a protein from fish with the name parvalbumin helped Parkinson’s patients to stop producing alpha-synuclein. PD patients suffer from clumping of alpha-synuclein, which causes their symptoms.
- Restriction of refined carbohydrates “especially diets with a low glycemic index, rich of vitamins and polyphenols, a Mediterranean diet for example, can be recommended”.
Regular exercise to prevent Parkinson’s disease
Regular physical exercise maintains body function and muscle strength. Dr. Emer MacSweeney said: “Being physically active is one of the best things you can do for your body. Exercise helps protect against many diseases and keeps the heart, muscles, bones, and brain in optimum condition. Exercise promotes the oxygenation of the brain and stimulation of multiple neurochemicals.”
Several studies showed that patients with PD deteriorate slower, if they exercise regularly. Part of that response is due to the release of endorphins and serotonin, but we do not know all of the positive mechanisms of exercise at this time.
Conclusion
Recent research changed what we know about Parkinson’s disease (PD). Braak’s Hypothesis of Parkinson’s Disease states that an unknown pathogen enters through the nose, gets swallowed and ends up in the gut. From there it gets taken up into the gut wall and migrates through the vagus nerve into the central nervous system. There it leads to accumulation of alpha-synuclein in the substantia nigra. This destroys the dopamine producing cells in that region causing the symptoms of PD. But we also know that chronic inflammation can aggravate the symptoms of PD patients. When the composition of the gut bacteria deteriorates, this too will make PD patients worse.
Lifestyle changes help to postpone Parkinson’s disease
A healthy diet, like the MIND diet, DASH diet or the Mediterranean diet have beneficial effects on PD patients. Many studies also found that regular physical exercise is a stabilizing factor in PD patients. There are still many gaps in what we know about the causation of PD. But the above summarized factors are a good start.