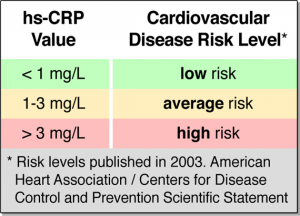
An old blood test that has been popular in assessing how aggressive rheumatic illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus are, is now considered as the newest test to assess the risk of heart attacks. Up to now subfractions of cholesterol, in particular the LDL cholesterol level, has been used to assess the risk for a heart attack, but this according to a new study in the New England Journal of Medicine (Nov. 14, 2002) by Dr. Paul Ridker should be supplemented by a blood test checking for the C-reactive protein. What is interesting about the C-reactive protein is that it originates from certain lining cells in blood vessels of liver tissue when inflammatory substances circulate in the body. Other research has shown in the past that arteriosclerosis is in part due to an inflammatory process in the lining of the blood vessels that leads to the production of the C-reactive protein. Unfortunately other chronic illnesses and infections also lead to an elevation of the C-reactive protein as does the common cold or the flu. However, when 28,000 women of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital study were followed for 8 years it turned out that the C-reactive protein was a more reliable predictor for who would eventually suffer from a stroke or a heart attack than the traditional LDL cholesterol. The investigators felt that the LDL cholesterol is predictive for who is more likely to develop fatty deposits (atheromatous plaques). On the other hand the C-reactive protein appears to be more predictive for who is at a high risk for rupture of these atheromatous plaques. The bottom line is prevention by eating a diet with less fatty meats, by eating more fruit and vegetables and by engaging in an exercise program.
Some patients need their cholesterol reduced with medication such as the statins. You may want to browse through these useful related links to chapters of my free Internet based Nethealthbook: For more details regarding the use of the C-reative protein test in rheumatoid arthritis see this link: http://www.nethealthbook.com/articles/rheumatologicaldisease_rheumatoidarthritis.php Regarding arteriosclerosis, heart attacks and strokes follow this link: http://www.nethealthbook.com/articles/cardiovasculardisease_heartdisease.php
Last edited December 10, 2012