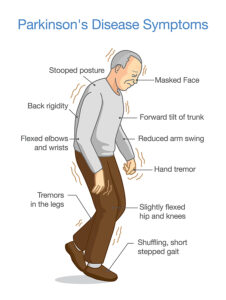
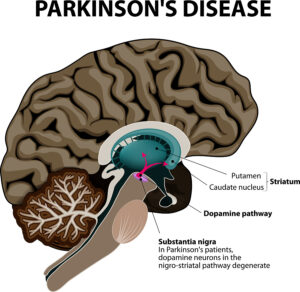
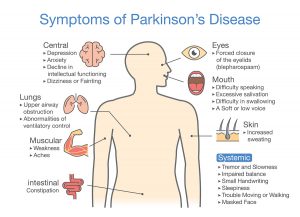
A new study describes how a spinal cord implant provides help to walk for Parkinson’s disease patients. The original study was published in Nature: . CNN published a simplified article that describes how a Parkinson’s patient with gait problems could walk again, when a spinal cord implant was inserted. This patient’s name is Marc Gauthier from a town near Bordeaux, France. He was 36 years old when he was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. For many years he could control his Parkinson’s disease symptoms with Dopamine replacement therapy.
Insertion of deep brain stimulator
But by 2004 the medication did not control his gait anymore. His doctors inserted a deep brain stimulator, which helped with tremors and muscle stiffness. But as the disease progressed, he developed a severe walking disorder. The drugs and the deep brain stimulator no longer helped his walking problem. His muscles stiffened up, and often he fell 4-times per day. He had to give up his work as an architect. Finally, in 2021 his doctors inserted a nerve stimulator with electrodes connecting to the lower spinal cord.
Spinal cord stimulation
Researchers from France, Switzerland and other parts of the world determined which part of the spinal cord were in need of electrical stimulation to improve his gait and balance problems. Dr. Eduardo Moraud is an author of the study and researcher at Lausanne University Hospital. He said: “The stimulation here is focused on the spinal cord. We target the region of the spinal cord that will control all the leg movements.” The team managed to develop an electric stimulator for implantation under the skin over the abdomen with electrodes going to the lower spinal cord. This way his physicians stimulated muscle groups and also relaxed them in sequence so that his gait improved and steadied. His balance stabilized as well and he could walk stairs again.
Future routine surgery to implant spinal stimulator
Marc Gauthier’s case is a first in approaching Parkinson’s disease with a spinal stimulator. The researchers stressed that they will improve the technology and learn from other patients how to individualize this technique. But eventually the spinal cord stimulator could become a routine approach for end stage Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Moraud said: “Addressing deficits of gait and balance in Parkinson’s disease is extremely challenging. These deficits can be very heterogenous. They can be variable across patients. They can affect walking but also symmetry, balance, posture. The neuroprosthetic approach that we have developed here allows for the first time to target and address these problems individually in a highly specific manner for each patient. It operates in real time, and importantly, it is complementary to other existing therapies.”
Marc Gauthier’s progress since his spinal cord stimulator
The researchers identified hotspots in the lower spinal cord with connection to the gait and balance problem of the patient. The surgeon connected the neuroprosthesis to these hotspots to stabilize gait, balance and muscle strength. Following the surgical procedure Mr. Gauthier had to undergo a few months of rehabilitation with the neurostimulator to practice walking, develop strength and coordination between the right and left leg. His body was no longer stiffening or freezing in place. He could now take a 3-mile lakeside stroll without stopping. He can now manage stairs going up or coming down smoothly. In the past his gait would suddenly freeze or he lost hist balance. None of this
Is happening now. He simply is walking normally.
The final word of Dr. Moraud
“The stimulation here is focused on the spinal cord. We target the region of the spinal cord that will control all the leg movements.” Inserting a neurostimulator is not a cure, simply a procedure to help the patient lead a normal life.
Conclusion
A new surgical procedure, namely inserting a neurostimulator under the abdominal wall, is the latest approach to treat Parkinson’s disease. This is help to walk for Parkinson’s disease patients. The case, which I described here is the first case where doctors performed this new procedure. They identified hot spots in the lower spinal cord and connected them to the neurostimulator with electrodes. After a lengthy rehabilitation period the patient learned how to use the stimulator for optimal walking, balancing, and going stairs up and down. There are no more falls or gait problems and no freezing. At the end the patient can walk normally and even manage a walk of 3 miles. Researchers anticipate that this method will become an accepted treatment modality for gait problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.