To women waist measurement has always been of importance. Increased waist measurement and weight gain go hand in hand, and a poor fitting garment in the waist usually signals to cut out the junk food. In the past century extremely tiny waists became an unhealthy obsession, till common sense got the upper hand.
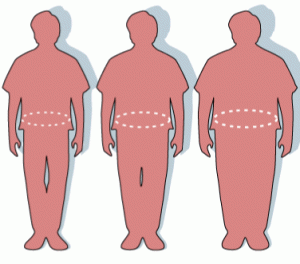
In the past males seemed to be unperturbed by a large girth and often ridiculed the opposite sex about their preoccupation with their waist lines. With more knowledge about the intricate play of metabolism increased waist circumference is a signal to health problems. It may be that a simple measuring tape can be one of the most helpful tools to predict a group of health problems in males. While type 2 diabetes, hypertension and high cholesterol and triglycerides are the problems that would first come to mind, there are more, namely coronary artery disease, prostate enlargement, a high prostate-specific antigen level, erectile dysfunction and ejaculatory dysfunction. Dr. Steven Kaplan, professor of urology at Cornell University, New York presented a study at the American Urological Association. Men with moderate to severe urinary tract symptoms were divided into groups based on their waist sizes, 30 to 36 inches, 36 to 40 inches and greater than 40 inches.
Results surprised even the researchers. Metabolic disorders like diabetes showed an incidence of 11.25% in the first group, 22.3 % in the next higher group and 37.8% in the group with waistlines over 40 inches. Erectile dysfunction was seen in 34.6%, 49.5% and 78.6 % respectively. The percentiles for hypertension showed 12.6% in the first group, versus 24.7% and 37.8 %. The researchers stressed that male pelvic dysfunction and the derailment of metabolic function, also known as the “metabolic syndrome” are closely linked.
More information about metabolic syndrome: http://nethealthbook.com/hormones/metabolic-syndrome/
Last edited November 2, 2014