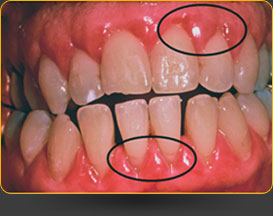
When people think of hazards to dental health, the first thought will be about tooth decay, lack of brushing and flossing and eating candies and other sugar-laden foods. Periodontal disease is often neglected, and yet it is just as threatening to teeth and gums. Destructive periodontal disease will lead to loss of the supporting tissues of the teeth and as a result, there will be loose or shifting teeth and ultimately tooth loss. Generally these findings were seen in older population groups. It was thought that the disease would rarely occur in patients younger than 35 years of age and the theory was that dental plaque was the likely cause. Lifestyle choices were not thought to play a large role. Recent findings told a different story. A cohort study consisting of 903 participants examined self-reported tobacco and marijuana smoking and dental examinations were also done. The authors of the study found that tobacco smoking as well as cannabis (marijuana) smoking was linked with a higher incidence of destructive periodontal disease before the age of 32 years.
In comparison to this dental plaque was not contributing to a higher incidence of periodontal disease in this younger age group. Another risk for destructive periodontal disease in the youngest age group (as young as 12 to 18 years of age) was impaired glucose intolerance (a condition leading to diabetes). Due to those findings it is obvious that brushing and flossing are not the only weapons against periodontal disease. Healthy eating habits and cessation of smoking are equally important for dental health. This is particularly important as heart disease, which is also an inflammatory condition is closely linked to inflammatory disease of the gums and you likely have heard that heart attacks can be prevented by brushing and flossing teeth.
More information about periodontal disease: http://nethealthbook.com/dentistry/periodontitis/
Reference: Journal of American Medical Association 2008; 299(5): pages 574-575
Last edited November 3, 2014