Nobody can predict when the next pandemic will hit and whether it will be from an avian flu, but Canada and other countries are not taking any chances. The feds have commissioned a mock vaccine that can be adapted to whatever strain comes along. The Canadian Public Health Agency is also calling for alertness to patients coming back from countries where avian flu has occurred, especially countries with human cases. Canada is erring on the side of caution when it comes to the national flu pandemic preparedness plan. There is preparation for up to 138,000 people in need for hospitalization and between 11,000 and 58,000 death could occur. The economic impact is estimated between $ 10 and 24 billion.
It is true that public health agencies are worried, as three conditions for a possible pandemic are present: the viral strain is a new one, humans have no immunity to this new virus, and the strain is virulent.
The fourth condition would be that the strain could be spread from person to person. However this condition has not developed at this point.
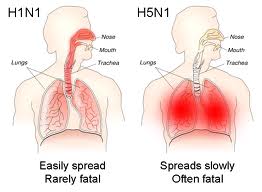
A lot of hype has gone through the press, misinformation is rampant, and as a result people are mixing up influenza preparedness with an avian flu pandemic. Anxiety runs high in the population. Some health professionals are already suffering from pandemic burnout before the virus has even landed, which is not a surprise: in the last few years warnings were sounded due to the outbreak of SARS. West Nile, Ebola, and Lassa fever have been other diseases that caused concern and anxiety. Before jumping to frightening conclusions that the avian flu will jump from person to person, it is important to see the facts in perspective. H5N1 at this point is not spread from person to person. The virus is transmitted from affected birds (chicken ducks, and other fowl) to humans, who have to be in close contact with the animal. The virus is found deep in the lungs of the infected person, and as a result it is more difficult to transmit than a virus that is found in mouth, nose or throat.
Human fatalities have occurred in Asia and the Middle East. Vietnam has had the highest number of deaths related to H5N1: 93 infections, 42 fatalities. Turkey has had 12 documented cases, four of them fatal.
In the meantime the world is not defenseless. Vaccines are in preparation, and vaccination trials are have been introduced in Vietnam. Work with horse antibodies is ongoing and the results are encouraging. Researchers in China developed a passive immunization by using horse antibodies. The advantage is the fact, that larger amounts of vaccine can be produced faster than with the culturing of the virus on eggs.
Public health agencies and health professionals are aware of the fact that pandemics have been around in the past. They are still a threat now. They agree that programs have to be in place to help mitigate the impact by doing the best they can. Disaster preparedness and alertness are definitely in order. Panic is not.
More information about other flus:
1. the Flu (influenza, H3N2): http://nethealthbook.com/infectious-disease/respiratory-infections/flu/
2. Swine flu (H1N1): http://nethealthbook.com/infectious-disease/respiratory-infections/swine-flu/
3. Bird Flu (H5N1): https://www.askdrray.com/worldwide-alert-for-avian-influenza-bird-flu/
Reference: National Review Of Medicine, March 30, 2006, page 5.
Last edited Oct. 31, 2014