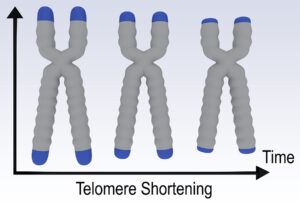
Longer telomeres can protect you from premature aging, and shorter telomeres lead to premature death and various diseases. But recently new research showed that sometimes longer telomeres can be responsible for cancer and lower life expectancy. I will discuss this further below.
Some facts about telomeres
Telomeres are the caps on the chromosomes that do not contain genes, but are important for cell division. When cells divide, the DNA with all the genetic information about us replicates. With cell division each copy of our DNA ends up in a new cell, but the telomere gets shorter with every cell division. The enzyme telomerase is able to lengthen our telomeres. A healthy Mediterranean diet, regular exercise, not smoking cigarettes, sleeping 7 or 8 hours every night are all factors that stimulate elongation of our telomeres. When telomeres are short, they can no longer divide, but the cells turn into senescent cells. They no longer divide, but they stay metabolically active and are significant in the diseases of the aging. They cause osteoarthritis, hardening of the arteries and cancer.
Mice with hyper-long telomeres live much longer than control animals and they have lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Animal studies confirm that short telomeres mean shorter lifespan
There were animal studies that showed that telomeres shorten more slowly in long-lived birds and mammals.
A study looked at the telomere shortening rates of different animal species. They found that those species that had the fastest telomere shortening rate were also the ones with the shortest life span.
Shorter telomeres can also cause several chronic health conditions.
Telomerase helps to keep telomeres from shortening
An important ingredient in every body cell is the enzyme telomerase. It attaches to telomeres and adds DNA to telomeres thus elongating them. Many healthy lifestyles increase telomerase and help shortened telomeres to get longer again.
What preserves the length of your telomeres?
I have previously reviewed factors that elongate telomeres. Here is a summary of this information.
Telomere length enhancers
- Lifestyle changes can have positive effects on telomere length. Examples are smoking cessation, weight loss and stress reduction.
- Dietary changes: we know that fish oil (omega-3 fatty acids) supplements elongate telomeres as does a low-fat diet.
- Supplements like vitamin D3, antioxidants (vitamin C and E) and astragalus (TA-65) elongate telomeres as well. The astragalus supplement, TA-65 showed a significant elongation of telomeres after 12 months while controls lost telomere length.
- Exercise: in a 24-week experiment of care workers regular aerobic exercise increased the telomeres by 67.3 base pairs.
- Bioidentical hormone replacement in aging people: when hormones are missing after andropause and menopause, the natural hormones need replacing, or the telomeres are shortening.
- High cortisol levels cause telomere shortening.
- Human growth hormone elongates telomeres via telomerase activation.
- The fasting mimicking diet (FMD) was shown to extend life and telomeres as well.
Conflicting research about longer telomeres
A publication in the New England Journal of Medicine dated May 4, 2023 showed that patients with a POT1 mutation had long telomeres. This mutation caused cancers, brain tumors, B- and T-cell lymphomas and bone marrow cancers. The long telomeres facilitated cancer growth. Normally this type of mutation is rare and in patients without this mutation long telomeres would lead to longevity.
Dr. Joshua Berkowitz, the Medical Director of IV Boost UK, said that further research needs to focus on the following: “Identifying genetic and epigenetic factors that contribute to aging and longevity, understanding the role of the microbiome in aging and longevity, and investigating the role of senescent cells in aging and age-related diseases.”
Conclusion
Our telomeres are needed for cell division. When telomeres get shorter with age there is a consensus that this leads to a potentially dangerous situation. The cells turn into senescent cells. They no longer divide, but they stay metabolically active and are causing the diseases of the aging. These are osteoarthritis, hardening of the arteries, cancer and many more. On the other end of the spectrum with regular exercise, a Mediterranean diet and a normal weight, telomeres can get elongated, which for most people means a longer life expectancy. However, recent research showed that patients with a POT1 mutation are vulnerable to facilitating cancer growth and premature death. Fortunately, the POT1 mutation is rare. Future research will clarify what the safest way is to achieve longevity.