The media has praised alcohol for preventing heart attacks, but let us examine what alcohol does to you. There are other articles in which we hear about alcoholic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis, both of which can be killer diseases. To get some clarification, let us discuss the various facts.
Dr. Finnel points out that 7.9% of all emergency room visits in the US are due to alcohol related conditions (Ref.1). When the causes of deaths that are a consequence to alcohol are listed, the top 8 causes are: cancer of the mouth and pharynx, alcohol abuse disorders, coronary heart disease causing heart attacks, cirrhosis of the liver, traffic accidents, poisonings, falls and intentional injuries. This is not what you read in the news. What you do read about is that one glass of red wine per day would be good for women and up to two glasses of red wine would be good for men to prevent heart attacks and strokes.
Bioflavonoids
It is the bioflavonoids , and among those in particular resveratrol, that are the active ingredients responsible for heart health. Resveratrol is a powerful antioxidant that protects against ischemia-reperfusion injuries. It is responsible for the cardio protective properties of red wine known as the “French paradox” (Ref.2). According to this reference resveratrol contributes to at least 3 processes that stabilize the metabolism.
Toxicity of alcohol
Alcohol toxicity is a complex problem. According to the WHO 5.3% of all deaths worldwide are a consequence to alcohol. In 2012 the WHO recorded that 7.6% of deaths in males were due to alcohol. In comparison, 4% of female deaths were due to alcohol. Toxicity comes from the breakdown product acetaldehyde, which all cells can convert from alcohol, but liver cells are especially able to do this. According to Ref. 3 alcohol diffuses easily through all of the cell membranes and reaches every organ in the body. The toxicity of acetaldehyde is the reason for shutting down the mitochondria which affect the energy metabolism and causing cell death. The immune system reacts with inflammation, when it attempts to repair the damage.
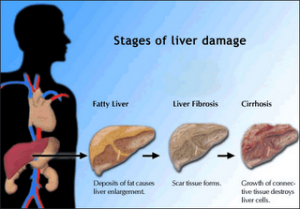
So, what are the major problems what alcohol does to you? These are the processes: First fat accumulation (steatosis), next chronic inflammation followed by necrosis (dying of cells) and fibrosis. An example of fibrosis is liver cirrhosis, where non-functioning connective tissue replaces liver cells.
Different tissue sensitivity to alcohol
Certain tissues are more susceptible to alcohol toxicity than others. As the concentration of alcohol is highest in tissues that are in direct contact with alcoholic drinks, cancers related to alcohol consumption develop in the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, and in the colon and rectum. The pancreas is particularly vulnerable to inflammation and fibrotic changes with subsequent degeneration into cancer of the pancreas. The heart tissue and the arteries are very sensitive to alcohol; hypertension, heart attacks, stroke, cardiomyopathy and myocarditis as well as irregular heart beats (arrhythmias) can develop. The brain is very sensitive to toxic effects of alcohol as well. This causes major depression, personality changes with violent behavior, car accidents and injuries.
Other toxic effects of alcohol on organs
Kidney disease (alcoholic nephropathy) is another alcohol caused illness. 5% of breast cancers in northern Europe and North America are directly related to the toxic effects of alcohol (Ref.3). Finally, the liver being so active in detoxifying alcohol is affected by developing liver cirrhosis, which accounts for a lot of premature deaths at a relatively young age (typically in the mid to late 50’s).
Ref. 3 goes on to say that literature exists which claims that 1 to 2 drinks per day would be useful for prevention of heart disease. But the observation of the authors is that people will not discipline themselves to stick to these limits and very quickly enter into the zone of alcohol toxicity. The authors further noted that with regard to causing any kind of cancer there is no safe lower limit; the risk is directly proportional to the amount of alcohol consumed and the risk starts right above the zero point.
The pathologist has the last word
When I studied medicine at the University of Tübingen, Germany I attended lectures in the pathology department where Professor A. Bohle, M.D. demonstrated pathology findings of deceased patients. Dr. Bohle had a special interest in Mallory bodies. These are alcohol inclusion cysts within liver cells that can be stained with a bright red dye.
Histological documentation of toxic effects in livers of corpses
I will never forget when Prof. Bohle pointed out that the livers of this most diverse population whose bodies we had the privilege as medical students to study had a rate of 25% positive Mallory bodies. He wanted to impress on us as medical students to watch out for the alcoholics that are usually missed in general practice. Obviously 25% of the pathology population was affected by the consumption of alcohol. It was Prof. Bohle’s hope that we could perhaps interfere on the primary care level before things went out of control. Many of these corpses belonged to traffic accidents that could have been prevented (now seat belts and alcohol limits are standard, in 1968 they were not).
Alcohol as an aging substance
Consistent use of alcohol on a regular basis will slow down cell metabolism and hormone production significantly. The major effect of alcohol leads to poisoning of the mitochondria in multiple organs, which translates into faster aging and a shortened life expectancy. This in turn results in a change of appearance. An older person who has abused alcohol for a number of years may look 5 to 10 years older than their chronological age.
50% of people above the age of 65 drink daily (Ref.4). Some more statistics: alcohol abuse in elderly men is 4-times higher than in elderly women. 5% to 10% of all dementia cases are related to alcohol abuse. About 15% of older adults are experiencing health risks from abusing alcohol. And about 90% of older adults are using medications and close to 100% of medications can adversely interact with alcohol (Ref.4).
Social pressure
These are the scientific facts , and then there is social pressure when you are invited to a party.
When you are young and invincible, do you care what the science says? You want to have a “good time” and not worry about consequences. The data about long-term exposure and a slowly increasing cancer risk is there. The wine industry will remind you that 1 drink for women and two drinks for men will protect you from heart attacks. They will withhold the cancer information from you, as they don’t really want to hear about that (yes, it’s bad for their business!).
Resisting social pressure and doing what is good for you
Can you have a good time at a party without drinking alcohol? Yes, you can. You can talk and you can listen; you are probably more with it than those who had too much to drink. I like mineral water and hold on to a glass of that.
I explained in a blog before how I was convinced by three speakers at an A4M conference to join those who abstain from alcohol.
Socializing without alcohol is doable. You may at times miss it, but you can warm up even to a crowd that had a few drinks too much. It is about choice: we can choose what we want out of life.
Conclusion
I have attempted to show you the toxic effects of alcohol. Although alcohol has played an important role in the social lives of millions over the centuries, it is becoming more apparent that alcohol is a cell poison and shortens our lives. The beneficial effect of the 1 or 2 drinks marketed by the beer and wine industry and some cardiologists does nothing to counter the threat in terms of a whole array of cancers at much smaller amounts of alcohol. Fortunately, resveratrol and omega-3 fatty acids as supplements as well as exercise will more than make up for the 1 or 2 drinks that you do not really need. And neither exercise, omega-3 fatty acids, or resveratrol are cell poisons. The choice is yours!
References
Ref. 1: John T. Finnell: “: Alcohol-Related Disease“ Rosen’s Emergency Medicine, Chapter 185, 2378-2394. Saunders 2014.
Ref. 2: “Hurst’s The Heart”, 13th edition, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2011. Chapter 54. Coronary Blood Flow and Myocardial Ischemia.
Ref. 3: Ivan Rusyn and Ramon Bataller: “Alcohol and toxicity”, 2013-08-01Z, Volume 59, Issue 2, Pages 387-388; copyright 2013 European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Ref. 4: Tom J. Wachtel and Marsha D. Fretwell: Practical Guide to the Care of the Geriatric Patient, Third Edition, Copyright 2007 by Mosby.