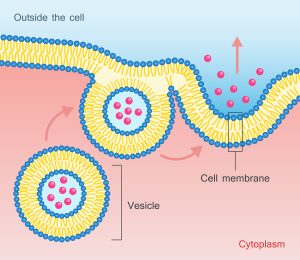
Dr. Douglas J. Spiel gave a talk on how exosomes can regenerate your stem cells. In essence, this was at the 27th Annual World Congress on Anti-Aging Medicine in Las Vegas from Dec. 13 to 15th, 2019. His original topic was: “Placental MSC Exosomes for Longevity and Chronic Disease”. Notably, MSC stands for “mesenchymal stem cells”. Dr. Spiel recommended this website to look at applications of exosome therapy.
Essentially, what scientist found is that certain factors from stem cells can activate your own stem cells to regenerate tissues that grow old. These factors are messenger RNA (mRNA) and micro RNA (miRNA), which come as tiny particles of 40‐100 nm.
Advantages of administering exosomes
To emphasize, exosomes can be given systemically as infusion, and they can regenerate your stem cells, if they are in need of treatment. They cross the blood brain barrier, so it is possible to treat brain diseases. That is to say, there is no first-pass removal in the lungs as it is with mesenchymal stem cells (MSC). The potency is related to the age of the donor and his/her stem cells. Notably, exosomes are easy to store, freeze and administer.
Exosomes influence the growth of target cells and promote regeneration. In addition, exosomes stimulate immunomodulation and have anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic properties. To clarify, the only limitations are that the strength of the exosomes is related to the age of the blood donor. The exosome fraction comes from mesenchymal stem cells. That is to say, it circulates in the plasma portion of the blood, which is obtained by spinning blood cells down in a centrifuge. To emphasize, exosomes can regenerate your stem cells.
Applications of exosomes for various clinical conditions
Joint inflammation
Mesenchymal stem cells are useful to treat arthritis. But it is important to realize that exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells are doing the same by stimulating the body’s own stem cells situated in the joints. In fact, several target cells have been identified that are stimulated by exosomes. These are chondrocytes, chondrocyte progenitor cells, cartilage-derived stem cells and synovium‐resident multipotent progenitor cells. In addition, other target cells are osteoblasts and osteoclasts in resident MSC within the subchondral bone and chondrogenic cells in the knee joint.
Disc degeneration
Degenerative intervertebral discs respond to exosome treatments. The IL1 beta cytokine is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exosomes inactivate these cytokines and have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Exosomes are not all the same. Different sub-fractions were isolated that have anti-inflammatory, immune-stimulating, antioxidant and other effects on the body.
Aging research
Researchers were able to pinpoint aging to various factors that contribute to premature aging. To clarify, when there is a decrease of catabolic processes and an increase of anabolic processes, an older person can combat premature senescence. Another key point, aging is also linked to redox homeostasis. Simply put, oxygenation processes in the body need to be balanced by reduction processes. This keeps the body in a healthy state. ADP/NADH production can be stimulated by exosomes.
Longevity comes from good lifestyles
With the use of exosomes, the aging process slows down, as oxidative stress is neutralized, damaged mitochondria are removed and cellular debris as well. That is to say, this improves inflammation and premature aging.
As has been noted, in the past 200 years life expectancy has doubled in most countries. 4 areas where longevity is particularly common are: Okinawa, Japan; Sardinia, Italy; Nicoya, Costa Rica and Loma Linda, USA. Only 7% of longevity stems from genetic factors, the rest is from lifestyles we adopt. In the final analysis, people who die prematurely followed a very poor lifestyle causing them to develop diseases, which ultimately killed them.
Clinical diseases from aging
Ultimately, advanced aging puts you at risk of getting cardiovascular disease (heart attacks and strokes), cancer and neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease). From the third decade onwards, there is the risk of bone loss, which causes osteoporosis. As has been noted, loss of cartilage causes osteoarthritis. Loss of muscle strength and muscle mass is called sarcopenia. With aging there is often an accumulation of abdominal fat. Hormones are disbalanced. Blood pressure is often elevated and blood lipids as well. Insulin resistance can develop and the blood vessels become stiffer. This causes heart attacks and strokes.
The details of the aging process are much more complicated than originally thought of. There is a combination of aging of the DNA, mitochondrial aging, stem cell exhaustion and a change of intercellular communication due to dysregulated endocrine signalling. In addition, there is a decline of the immune system and epigenetic factors that can turn off longevity genes.
Oxidative stress as a cause of premature aging
Dr. Spiel pointed out that reactive oxidative species (also known as free radicals) cause damage to mitochondria and mitochondrial DNA. But we need the energy from the mitochondria for a comfortable life. In essence, antioxidants can neutralize free radicals. Age-related conditions due to oxidative stress are: cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer, neurodegenerative disease, frailty and sarcopenia. Surely, both reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen are free radicals. They have one or more unpaired electrons and all aerobic body cells produce them. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) cause oxidative damage to our cells and contribute to the development the diseases just mentioned.
Antioxidants help to prevent diseases
But antioxidants can contain these free radicals in various ways. The body has five built-in enzymatic ways to protect itself and five non-enzymatic ways (bilirubin, vitamin E, beta-carotene, albumin and uric acid). In addition, there are antioxidants that a person can take as supplements to inactivate RONS. These are: vitamin C and E; phenolic antioxidants like resveratrol, phenolic acids, flavonoids, oil lecithin, selenium, zinc and drugs like acetylcysteine.
Without control of the oxidative stress RONS can lead to cellular senescence and chronic inflammation. This leads to a vicious cycle where chronic oxidative stress and inflammation feed on each other leading to premature diseases.
Causation of several diseases
As we age, the body reduces the inborn antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase). Before we can understand how to live longer, we need to be aware what happens in various health scenarios as follows.
- The lack of inborn antioxidant enzymes leads to vascular endothelial dysfunction, high blood pressure and premature hardening of the arteries. This can become a precursor to heart attacks and strokes.
- Elevated blood sugar in the case of type 2 diabetes leads to increased sugar concentration of body cells and formation of free radicals.
- Oxidants from cigarette smoke activate macrophages and epithelial cells to produce inflammatory cytokines. Continued smoking releases proteases in the process that break down connective tissue and cause emphysema and COPD.
There are more diseases
- Chronic kidney disease comes from oxidative stress affecting the filter units of the kidney, called glomeruli. With a lack of blood supply to the kidneys secondary high blood pressure develops and endothelial dysfunction. It also leads to chronic inflammation.
- In the brain oxidative stress leads to cognitive impairment and dementia.
- Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation are important ingredients for the development of cancer. RONS and cytokines release NF-kB, which activates cancer genes. RONS can also directly attack the DNA of cells and cause cancer through carcinogenesis.
- Sarcopenia and frailty come from the action of RONS on the skeletal muscles. In old age there are less inborn antioxidants available. This leads to decreased muscle quantity or sarcopenia. Eventually frailty results with the risk of falls and fractures.
Preventative measures for slowing the aging process
There is a number of steps that in combination help to slow the aging process.
- A Mediterranean diet combined with a fasting mimicking diet or other calorie restricted diet
- Regular physical activity
- Cognitive training
- Vitamin D3 supplementation
- Reducing your risk to develop vascular disease
- Certain drugs turn on the longevity gene (metformin, rifampin)
- Spiel warned that due to limited compliance and variable response these steps alone may not be enough to prevent age-related problems
How to live longer
It is important to recognize the importance of antioxidants to counteract the development of these diseases. As already mentioned, the following counter the effect of free radicals: vitamin C and E; phenolic antioxidants like resveratrol, phenolic acids, flavonoids, oil lecithin, selenium, zinc and drugs like acetylcysteine. Mesenchymal stem cells can also stop the action of free radicals. In addition, exosomes, which are products of mesenchymal stem cells can do the same. Mitochondria, the power houses within the cells, create energy, but also release free radicals. In his clinic Dr. Spiel administers intravenous exosomes to counter the oxidative stress. Numerous studies linked mitochondrial dysfunction to various age-related diseases. There are markers in blood tests that the physician can order to analyze malfunctions in the body. Dr. Spiel showed 4 slides that contained a lot of medical information that is too technical. I omitted it for this review.
Intravenous infusions of exosomes
The important thing to remember is that epigenetics can be changed by exosome infusion and lifestyle changes mentioned above. Dr. Spiel said that generally he uses 15 ml of exosomes by intravenous infusion every 12 weeks for longevity and performance enhancement. This treats conditions like infertility, osteoporosis, osteopenia, heart, liver and kidney weaknesses. Here is the dosing for intravenous exosomes by weight:
20-50 lb: 5 ml; 50-90 lb: 10ml; more than 90 lb: 15 ml; more than 220 lb: 20 ml. Unfortunately, one exosome treatment costs between 500.00 and 922.00 USD, an amount that most people cannot afford.
Contraindication to the use of stem cells or exosome therapy
It is important to realize that a person who has cancer should not receive either mesenchymal stem cells or exosomes. Indeed, exosomes do not differentiate between cancer cells and healthy cells, but stimulate cell division. For the same reason people with myeloproliferative disease (sickle cell anemia, bone marrow dysplasia) should also not receive exosomes. To clarify, other conditions where the physician will not order exosomes are primary pulmonary hypertension, acute bacterial infection or an immune-compromised state. In addition, macular degeneration with neovascularization is also a condition where the health professional does not administer exosomes.
Conclusion
Dr. Douglas J. Spiel gave a talk on how exosomes can regenerate your stem cells. Specifically, this was at the 27th Annual World Congress on Anti-Aging Medicine in Las Vegas from Dec. 13 to 15th, 2019. Dr. Spiel explained how disease processes age our organs. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) cause oxidative damage to our cells and contribute to the development of diseases. This involves the mitochondria in the cells as well. The good news is that a healthy lifestyle can counter these damaging processes to a certain extent. But it takes another step to re-establish the balance of our cells, exosome infusions. Exosomes are tiny particles that are shed by stem cells and that circulate in the blood. They can reenergize stem cells that are ailing to become functional again.
Expensive exosome infusions
He recommended an infusion with exosomes every 12 weeks for maintenance of good health and as a “fountain of youth”. Obviously, there are some limitations. As mentioned, it is not suitable for all patients, like cancer patients, patients with sickle cell anemia, acute bacterial infections or pulmonary hypertension. In addition, it is also not a treatment which many patients will seek out as the cost is prohibitive. One exosome treatment cost between 500.00 and 922.00 USD, an amount that most people cannot afford.