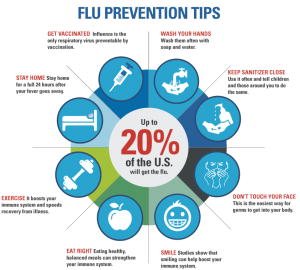
When we are young, we do not think about our immune system, but the immune system changes with age. When we are older than age 60, we notice that we may be taking longer to recover from a flu.
How does the immune system work?
There are two parts to the immune system, the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The innate immune system works to protect us from bacteria, viruses, toxins and fungi from the time we are born. The adaptive immune system uses B lymphocytes from the bone marrow to produce antibodies against viruses. This provides often lifelong immunity against this specific virus, but takes 3 to 5 days to kick in. Vaccinations can also trigger antibody production to protect us from viruses in the future. Both the adaptive and the innate immune system work together closely.
What are the ingredients for a fully functioning immune system?
The immune system consists of various immune organs that are distributed throughout the body. The bone marrow produces lymphocytes, granulocytes, macrophages, eosinophils and basophils. The adenoids in the back of the nasal passages and the tonsils in the back of the throat contain a lot of lymphocytes that are ready to protect us from colds and flus. We have lymph nodes throughout the body and they are connected with lymphatic vessels. The lymph nodes filter the lymph fluid that travels in the lymphatic vessels.
Other sites of lymphocyte production
The small intestine contains the Peyer’s patches, a collection of lymphocytes that protect our gut from invading bacteria or viruses. The spleen is located in the left abdominal cavity under the diaphragm. It removes old red blood cells and provides lymphocytes for the immune system. The thymus gland is located between the breast bone and the trachea. It changes bone marrow derived lymphocytes (B cells) into T lymphocytes that can process antigens from viruses and pass them on to the adaptive immune system for a full antibody response.
Cellular interactions between various players of the immune system
Back in the 1970’s it was already known that there were bone marrow derived B lymphocytes and thymus processed T lymphocytes. We knew then that B cells were involved in antibody production (adaptive immunity). T lymphocytes were thought to turn into killer T lymphocytes to kill cancer cells. But some T cells were T helper cells to process antigen and present it to B lymphocytes for antibody production.
More research since then refined what we know about the cells of the immune system.
Natural killer cells (NK cells)
Natural killer cells (NK cells) are part of the innate immune system. They attack cancer cells and cells that are infected by viruses. It takes about 3 days for their full action to develop. NK cells utilize the cell surface histocompatibility complex to decide whether to destroy a cell or not. T cell lymphocytes do not have the ability to do that. In the Covid-19 coronavirus situation NK cells play an important role to combat the disease right away.
Monocytes
They are large white blood cells that can differentiate further into macrophages and dendritic cells. Monocytes are part of the innate immunity, but they have an antigen presenting capability, which makes them also part of the adaptive immunity.
Memory T cells
The immune system learns to adapt to viruses and bacteria that we have come in contact with. The reason for the memory of the immune cells are the memory T cells. They replicate like stem cells, which keeps a clone of T lymphocytes, T helper cells and cytotoxic T killer cells in the background. They circulate through the body including the lymph glands and the spleen.
Immunosenescence as we age
There are several factors that come together, which age our immune system. The term for this is “immunosenescence“. There are genetic differences and differences due to the sex hormones. Estrogens increase the response of the immune system. In contrast, progesterone and androgens (including testosterone) decrease the immune response. This may be the reason why women tend to live longer than men.
As we age there are more and more memory T cells (both cytotoxic T cells and T helper cells). This weakens the formation of the natural killer cells (NK cells) of the innate immune system. Even the initiation of the adaptive immune system can be slower when we age and also the response to the flu vaccine. In addition, this can pave the way to autoimmune diseases.
The immune system changes with age: Evidence of immunosenescence
The following 3 factors show whether a person has immunosenescence:
- The immune system has difficulties to respond to new viruses/bacteria or to vaccines
- Accumulation of memory T cells crowding out cells of the rest of the immune system
- Low-grade inflammation that is chronic and persists (“inflamm-aging”)
The process of immunosenescence starts with the involution of the thymus gland around the time of puberty. At that time the sex hormone secretion is highest. At the same time a growth factor from the bone marrow and the thymus gland decreases. It has the name interleukin-7 (IL-7). The end result is a slow decrease of the innate immune system with age and a more substantial weakening of the adaptive immune system due to a lack of naïve T and B cells.
Chronic viruses can weaken the immune system further
The varicella herpes zoster virus causes chickenpox. In some people the chickenpox virus can persist, but the immune system actively keeps it controlled. In the 60’s or 70’s when the immune system is weakened from aging, there can be a flare-up as shingles, a localized form of the chickenpox virus.
Another virus, the human cytomegalovirus can cause a chronic infection that often persists lifelong. In this case the immune system is chronically weakened because of a massive accumulation of T memory cells, which keeps the human cytomegalovirus infection at bay.
What we need when the immune system changes with age
Vitamin A
Both the innate and adaptive immunity depend on vitamin A and its metabolites. The skin cells and mucosal cells function as a barrier, which is important for the innate immunity. The skin/mucosal lining of the eye, the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts help the innate immunity to keep viruses and bacteria out of the body. Vitamin A is important to support macrophages, neutrophils and natural killer (NK) cells. In addition, vitamin A supports the adaptive immune system, namely T and B lymphocytes, so that the body can produce specific antibodies against viruses.
I do not take vitamin A supplements as I eat diversified foods like spinach, vegetables, poultry, Brussels sprout, fish and dairy products that contain vitamin A and carotenoids.
Vitamin C
This vitamin is a powerful antioxidant. It can neutralize reactive oxygen species, which are produced when the immune cells fight viruses and bacteria. Neutrophils, lymphocytes and phagocytes are all supported by vitamin C. Vitamin C and E co-operate in their antioxidant functions. Vitamin C is essential for a strong antibody response with bacterial or viral infections. I take 1000 mg of vitamin C once daily.
Vitamin D
The immune system is very dependent on vitamin D as the immune cells all contain vitamin D receptors. People who have less than 10 ng/mL of vitamin D in the blood are vitamin D deficient. They have much higher death rates when they get infected with the Covid-19 coronavirus.
Vitamin D regulates the expression of target genes. At the center is the vitamin D receptor, which is a nuclear transcription factor. Together with the retinoic X receptor (from vitamin A) the vitamin D receptor binds small sequences of DNA. They have the name “vitamin D response elements” and are capable of initiating a cascade of molecular interactions. The result is a modulation of specific genes. Researchers identified thousands of vitamin D response elements that regulate between 100 and 1250 genes.
You need enough vitamin D for your immune system
When enough vitamin D is present in the blood (more than 30 ng/mL) the immune system releases the peptides cathelicidins and defensins, which effectively destroy bacteria and viruses.
Vitamin D has mainly an inhibitory function regarding adaptive immunity. It inhibits antibody production from B cells and also dampens the effect of T cells. Researchers reported that vitamin D3 is useful in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
I am a slow absorber of vitamin D3 as repeat blood vitamin D levels showed. I need 10,000 IU of vitamin D3 daily to get a blood level of 50-80 ng/mL (=125-200 nmol/L). This is the higher range of normal. Everybody is different. Ask your physician to check your blood level of vitamin D. Toxic vitamin D blood levels are only starting above 150 ng/mL (= 375 nmol/L).
Vitamin E
This is a vitamin that is fat soluble and helps the body to maintain its cell membranes. But researchers found that vitamin E also stimulates the T cell-mediated immune response. This is particularly important for the aging person to prevent respiratory tract infections. I take 125 mg of Annatto tocotrienols per day (this is the most potent form of vitamin E).
Vitamin B6
This vitamin is important for antibody production by B cells. Vitamin B6 regulates the metabolism of amino acids, which in turn form proteins. Antibodies and cytokines require vitamin B6. The T helper immune cells that initiate an adaptive immune response depend on vitamin B6 as well. I take a multi B complex vitamin (Mega B 50) twice per day, so I supplement with a total of 100 mg of vitamin B6 daily.
Folate
Folic acid is a coenzyme for the metabolism of nucleic acids and amino acids. Studies in humans and animals have shown that folate deficiency leads to increased susceptibility to infections. People with folate deficiency develop a megaloblastic anemia with immune weakness that leads to chronic infections. With my B complex supplement I get 2 mg of folic acid daily.
Vitamin B12
Methylation pathways depend on vitamin B12 as a coenzyme. Vitamin B12 is also involved as a coenzyme in the production of energy from fats and proteins. In addition, hemoglobin synthesis depends on vitamin B12. Patients with vitamin B12 deficiency develop pernicious anemia. These patients also have a weak immune system due to natural killer cell activity suppression and because circulating lymphocyte numbers are significantly decreased.
Treatment with cyanocobalamin reverses the immune weakness rapidly and treats pernicious anemia at the same time. I take 50 micrograms twice per day as part of the Mega-B50 multivitamin tablet. But I also inject 1000 micrograms of vitamin B12 every 6 months subcutaneously to be sure it is absorbed into the body. In older age the intrinsic factor from the stomach lining, which is required for absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine, can be missing, leading to vitamin B12 deficiency despite swallowing supplements.
Minerals required for a good immune response
Researchers identified five minerals that are essential for a strong immune system. They are zinc, iron, selenium, copper and magnesium.
Zinc
Zinc is important for a normal function of the innate and adaptive immune system. As zinc cannot be stored in the body, taking regular zinc supplements (30 to 50 mg daily) is important. I take 50 mg of amino acid chelated zinc daily.
Iron
Iron is important for cell oxygen transport and storage, DNA synthesis and for mounting an effective immune response. In particular it is the T cell differentiation and proliferation where iron is needed. Iron deficient people get a lot of infections because the immune system is paralyzed. I eat one spinach salad or steamed spinach daily, which gives me enough iron supply per day.
Selenium
Selenium is a trace mineral that is important for a normal immune response and for cancer prevention. When selenium is missing, both the adaptive and innate immune system are suffering. In this case viruses are more virulent. With selenium supplementation cell-mediated immunity is improved and the immune response to viruses is more potent. I take 200 micrograms of selenium per day.
Copper
Deficiency in copper results in a very low neutrophil blood count and causes susceptibility to infections. Copper is a trace mineral that participates in several enzymatic reactions. It is important for the innate immune response to bacterial infections. A well-balanced Mediterranean diet contains enough copper, which is why I do not supplement with extra copper.
Magnesium
An important cofactor for vitamin D in the body is magnesium. Magnesium participates in many enzymatic reactions. Between vitamin D and magnesium, the immune system is strengthened. I take 150 mg of magnesium citrate twice per day. By the way, magnesium also helps us to get a restful sleep, if we take it at bedtime.
Other dietary factors that strengthen the immune system
Polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids
It is important to note that polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids are essential for the body and help to modulate the immune system. I take 1800 mg of omega-3 (EPA/DHA) twice per day. I also like to eat fish and seafood at least 3 times per week.
Probiotics
Prebiotics benefit both the innate and the adaptive immune system. They strengthen the epithelial gut barrier, which is an important innate immune defence. Probiotics also lower the risk for Clostridium difficile gut infections. I take one probiotic every morning.
Conclusion
The immune system consists of different organs like the bone marrow, the spleen, lymph glands, Peyer’s patches in the gut, the thymus gland and more. There is the innate immune system, which responds immediately to a virus like the Covid-19 coronavirus. The adaptive immune response involves antibody production against, for instance, the measle virus or the mumps virus. With the aging process the immune system slows down (immunosenescence). This involves an accumulation of memory T cells and a depletion of natural killer cells (NK cells). This means that the innate immunity is getting weaker as we age and chronic inflammation occurs more often. This is the reason why people above the age of 65 get more severe symptoms from the Covid-19 coronavirus. They are also more affected by influenza-type illnesses.
Take supplements to strengthen the immune system
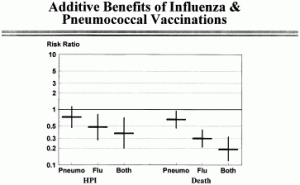
I reviewed the cofactors of a healthy immune system in some detail. It is important that you pay attention to these, particularly the vitamin D3 intake. With a strong immune system, we can survive viral infections better, including the current Covid-19 coronavirus. Future research will likely detect how to reactivate a sluggish immune system in older people. This way vaccination responses following flu injections will become more reliable in seniors.